Alternate Function Low Register vs Alternate Function High Register for an STM32F4xx Discovery Board
In this article, we go over the alternate function low register and the alternate function high register for an STM32F4xx discovery board.
So both of these registers are used when you are setting the mode for a GPIO pin in alternate function mode to determine exactly what alternate function the GPIO pin will have.
Before we go more into this, know that each GPIO PORT has 16 pins that go from pin 0 to pin 15. This is important to know when dealing with the alternate function low register and the alternate function high register.
This is because the alternate function low register is when you are dealing with the GPIO pins 0 to 7 of a given port.
The alternate function high register is when you are dealing with the GPIO pins 8 to 15 of a given port.
So if you are dealing with pins 0 to 7 of a GPIO port, you set the function for that pin with the alternate function low register.
If you are dealing with pins 8 to 15 of a GPIO port, you set the function for that pin with the alternate function high register.
To examine this with more depth, let's look at the diagrams for both of these registers.
Below is the diagram for the GPIO alternate function low register.
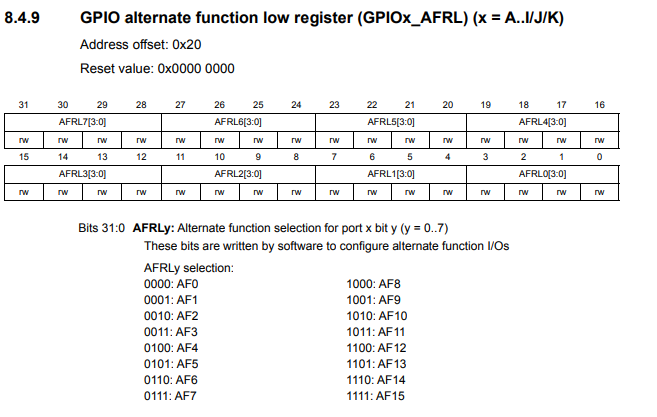
As all registers with the STM32 microcontrollers, each of these registers are 32 bits.
You can see that pins 0 to 7 are referenced and each pin is allocated 4 bits.
The reason each pin is allocated to 4 bits is because there are 16 possible alternate functions for each pins (even though this bits are simply reserved). So each of the pins can be placed in any 1 of 16 modes to determine what alternate function a pin will have. Since each pin is allocated to 4 bits to address the 16 possible alternate functions and there are 32 bits, then the register can only address 8 pins (0 to 7).
Therefore, it was decided by the manufacturer to have an alternate function low register (for pins 0 to 7) and an alternate function high register (pins 8 to 15).
Let's now look at the diagram for the GPIO alternate function high register.
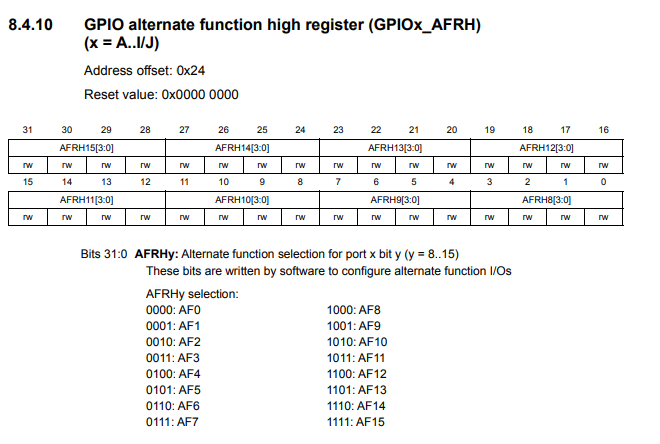
You can see that that the high register references pins 8 to 15. It's exactly the same in which 4 bits are allocated to each pin to address 16 possible alternate functions for each pin.
Answer: You would lose the alternate function low register, since this pin 2 is between pins 0-7.
Examples
So let's say you want to use pin 2 of GPIO PORTA as an alternate function pin, which register would you use?
Answer: You would lose the alternate function low register, since pin 2 is between pins 0-7.
So let's say you want to use pin 8 of GPIO PORTA as an alternate function pin, which register would you use?
Answer: You would lose the alternate function high register, since pin 8 is falls in the range of pins 8-15.
So this is the difference between the alternate function low register and the alternate function high register when used with an
STM32F4xx discovery board.
Related Resources
How to Set Bits of a Number in C
How to Clear Bits of a Number in C
