Troubleshooting- Transistor Turns On Without Any Base Current or Gate Voltage

You only really learn electronics when you actually build circuits and look at the real-life result.
When I was building a touch sensor circuit after I hooked up the circuit, I connected a LED to the output of the transistor, and the LED turned on, and I had connected no power to the base of the transistor.
I thought the transistor maybe was defective, so I swapped it out for another. Yet the same thing occurred. It conducted and turned on the LED without any base current. From what I knew before, transistors only could conduct when current was fed to the base of the transistor for bipolar junction transistors or voltage to the gate for mosfet transistors.
However, it turns out that transistors can conduct and power on even when there is no power to the base or gate of the transistor.
If too much voltage is fed into the collector of BJT transistors or the drain of mosfet transistors, the collector-emitter barrier or the drain-source barrier will break down and conduct current across. So this means even if no power is supplied to the base or gate, the transistor will still conduct.
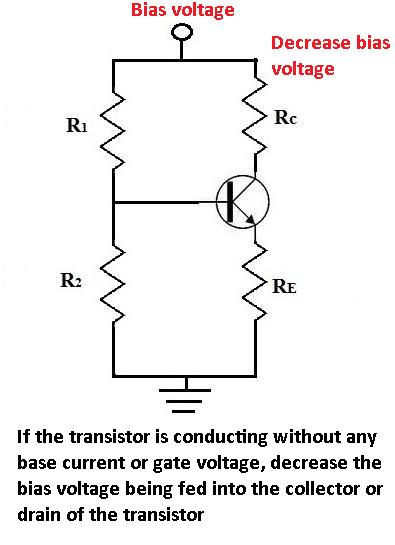
If a transistor is conducting without any power to the base or gate, this means that too much bias voltage is being used to the collector or drain of the transistor. The solution is to lower the bias voltage.
You have to make sure not to use too much bias voltage, or else the transistor will break down
and conduct across without any current or voltage needed on the base or gate.
This is something I discovered with simple experimentation with transistors.