How to Calculate the Base Current, IB , of a Transistor
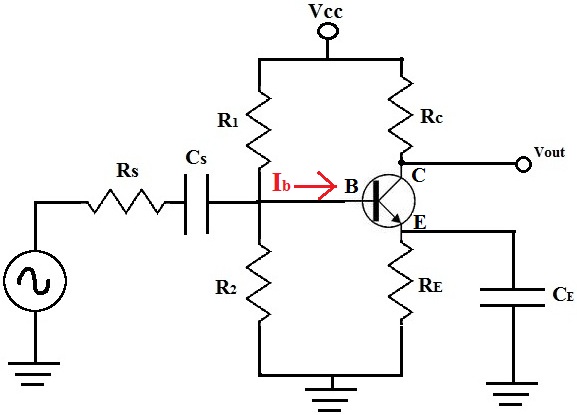
The base current, IB, of a transistor is a crucial current of a bipolar junction transistor. Without this base current, the transistor can't turn on.
There are several ways to find the base current, IB, of a transistor. And
it all depends on what information is already known about the transistor:
1st Way To Calculate Base Current IB
DC Analysis
Doing DC analysis of the transistor circuit is the most common way of finding out the value of IB in the circuit.
The equation to solve for Ie is:
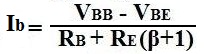
So we must solve for Vbb and RB in order to solve for IB.
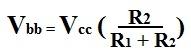
Next we compute the value of RB:
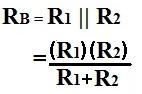
Now we can calculate the value of the base current, IB, in the circuit:
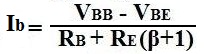
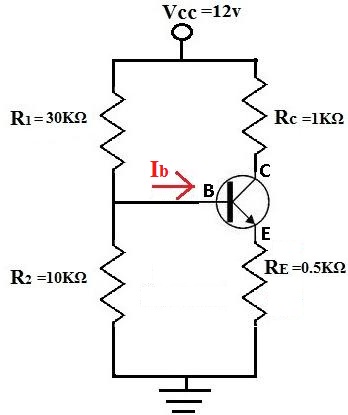
Example
Using the example of the values for the resistors and the voltage, Vcc, above, we're going to solve for Ieq.

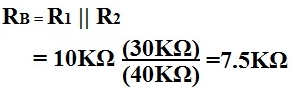
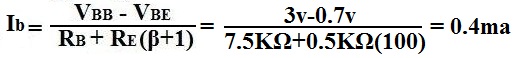
2nd Way to Calculate Base Current IB
Using Known Values
If the emitter current, Ie, and β are known for the transistor circuit, IB can be calculated by the formula:
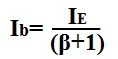
Example
If Ie=6ma and β=99, then
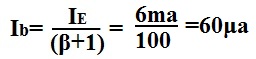
3rd Way to Calculate Base Current IB
Using Known Values
If the emitter current, Ie, and the collector current, Ic, are known, IB can be calculated by the formula:
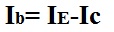
Example
If Ie=4ma and Ic=3.96ma, then IB calculates out to be:
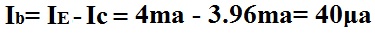
Related Resources
How to Calculate the Collector Current IC of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate the Emitter Current IF of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate β of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate α of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate VBB of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate VCE of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate Vπ of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate Rπ of a BJT Transistor
How to Calculate GmVπ of a BJT Transistor Circuit
How to Calculate GM of a BJT Transistor
