Inductor Reactance

The reactance of an inductor is how the impedance (or resistance) of the inductor changes in regard to the frequency of the signal passing through it.
Inductors, unlike resistors, are reactive devices. This means that they offer different resistances to signals of differing frequencies. To high-frequency signals, inductors offer a lot of resistance, so that high-frequency signals are essentially blocked from passing through an inductor. As the frequencies of the signals passing through an inductor decrease, the inductor offers less and less resistance, so that lower frequency signals can pass through easier.
The formula for calculating inductor reactance is:
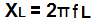
XL is equal to the value of the inductor reactance or impedance.
You can see, according to this formula, how inductor reactance changes according to the frequency of the signal input
into it. It has an direct relationship with the frequency of the signal passing through it.
The higher the frequency of the signal, the higher the
value of the reactance. The lower the frequency of the signal, the lower the value of the reactance.