Patau's Syndrome- Trisomy 13
Patau's syndrome is a genetic or chromosomal disorder in which an individual has 3 chromosomes in the 13th set of autosomes, instead of the normal amount of 2 chromosomes.
In human beings, a normal, healthy individual has 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Each pair out of these 23 sets (again, in a normal individual) consists of 2 chromosomes, for a total amount of 46 chromosomes.
However, an individual with patau's syndrome has an extra chromosome in the 13th set of autosomes, so, in total, has 47 chromosome. An individual
with patau's syndrome can be male or female. Being that an individual has an extra chromosomes in one of its set, this is an abnormality and leads to developmental issues such as
microcephaly, microphthalmia, usually blindness, heart defects, cleft lip and palate; all these issues will be explained and talked in more in-depth below.
Chromosomes of a Normal Healthy Individual
To show the contrast between a normal individual who has 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes and an individual with patau's syndrome who has 47 chromosomes, we will look at the karyotype of both individuals, which shows the profile of each's chromosomes.
Below is the karyotype of a normal and healthy male individual:
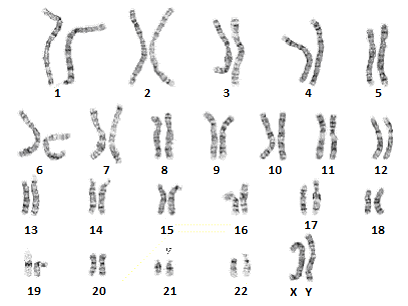
You can see the 13th set, as they are numbered above, with 2 chromsomes. This is the amount of chromosomes that a normal individual has who has no irregularities in
genetic make-up.
Patau's Syndrome- Trisomy 13
However, a few individuals are born not with 2 chromosomes in their 13th set, but with 3 chromosomes. They are individuals with an extra chromosome in their 13th autosome set.
This is the reason why patau's syndrome is referred to also as trisomy 13. Because in the 13th set, there are 3 (tri) chromosomes.
Below is the karyotype of an individual with patau's syndrome:
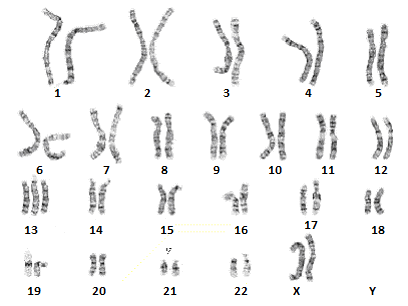
You can see the extra chromosome present in the 13th set of autosomes.
Symptoms of Patau's Syndrome
The symptoms that result from an individual who has patau's syndrome are microcephaly, microphthalmia, usually blindnesss, heart defects, cleft lip, and cleft palate.
- Microcephaly (my-kroh-SEHF-uh-lee)- Microcephaly is a neurological condition in which the circumference of an infant's head is significantly smaller than the heads of other people of the same age and sex. It is a rare condition, but as patau's syndrome is very rare, it correlates.
- Microphthalmia (my-krahf-THAHL-mee-uh)- Microphthalmia is an eye abnormality that arises before birth in which one or both eyeballs are abnormally small.
- Blindness- Many infants who have patau's syndrome usually are blind.
- Heart Defects- Usually infants who have patau's syndrome have heart defects, which significantly shortens their life. This is one of the reasons why children born with this syndrome usually don't live past 2 years of age.
- Cleft Lip- Cleft lip is a congenital split in the center of the upper lip.
- Cleft Palate- Cleft palate is a split of the palate, which is the top of the roof of the mouth of an individual.
Below is a picture of an infant with patau's syndrome:
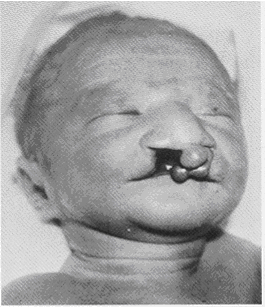
You can see how this baby has small eyes, a cleft lip and palate.
Incidence of Patau's Syndrome
The incidence of individuals having patau's syndrome is 1 out of 20,000 live births.
References
http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/microphthalmia
Related Resources
Down's Syndrome
Edward's Syndrome
Turner's Syndrome
Klinefelter's Syndrome
Supermale- XYY Syndrome
Superfemale- XXX Syndrome
