What Happens When the Voltage Supplied to a Zener Diode is Less Than Its Rated Voltage?

We all know that if you supply voltage to a zener diode above its regulated voltage, the voltage will stay constant at the regulated voltage.
For example, if we have a zener diode that is rated for 4.7V, and we feed it 5V or higher, it will stay at 4.7V.
You should always put a resistor in series with the zener diode so that any excess voltage then falls across the resistor. With this setup, which can be seen below, if more voltage is fed across the circuit, the voltage across the zener diode stays constant, while the voltage across the resistor would increase.
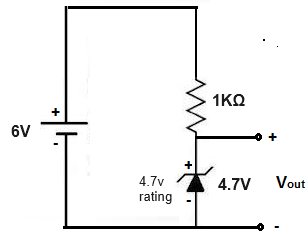
Now what will happen when the voltage to the circuit falls below the rated voltage of the zener diode? What happens to the voltage across the zener diode.
I ran this test by actually setting up the circuit.
If, for example, with the same zener diode rated for 4.7V, the circuit only is supplied 3V, what happens?
In this situation, almost all of the voltage falls across the zener diode. Therefore, almost all 3V will fall across the zener diode and practically none across the resistor.
What would this be the case?
Remember, according to ohm's law, that voltage divides in a circuit according to resistance.
When a zener diode is in reverse biased, its resistance is very high. I used a multimeter on an 1N4732 zener diode, which is a zener diode that is rated for 4.7V, the resistance was 6.39MΩ. (The resistance in forward biased is also high at 0.57MΩ, but we always connect a zener diode in reverse biased).
So, in reverse biased, with a resistance of 6.39MΩ, in series with a 1KΩ resistor, easily the vast majority of the voltage falls across the zener diode.
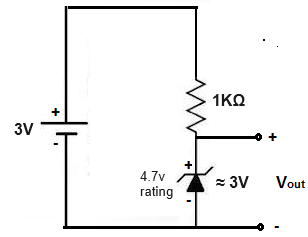
This means that if we feed the circuit 3V, we can expect around 3V across the zener diode.
This is shown below.
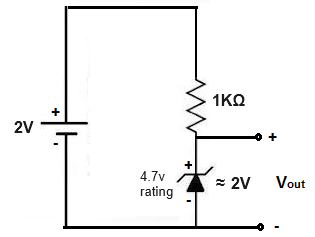
If we feed the circuit 2V, we can expect around 2V across the zener diode.
The 1KΩ resistor will really only have voltage when the voltage rises above the level of the zener diode.
The 1KΩ resistor acts to then absorb the excess voltage in the voltage divider.
And this is what happens when the voltage supplied to the zener diode falls to less than the rated voltage of the zener diode.
Related Resources
