What is the Breakdown Voltage, BVDS , of a FET Transistor?
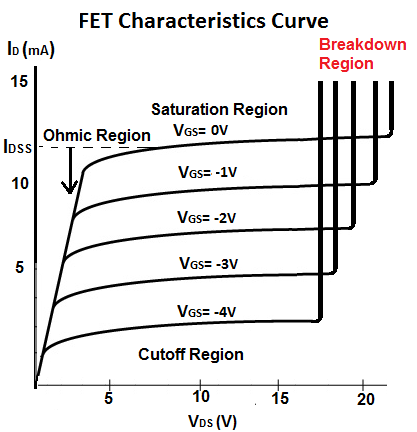
The breakdown voltage, BVDS, of a FET transistor is the drain-source voltage, VDS, which causes the transistor to enter the breakdown region; this the region where the transistor receives too much voltage across its drain-source terminal, which causes the drain-source terminal to break down, which makes the drain current, ID, drastically increase.
The breakdown region, which the breakdown voltage causes the transistor to enter, is the last section (to the right) of the FET characteristics curve. In this region, the drain-source voltage, VDS increases too much for the channel to handle. At this point, the FET loses its ability to resist current because too much voltage is applied across the drain-source terminal.
The breakdown voltage, BVDS of a FET transistor, can range in value anywhere from 6V to 50V. Check the datasheet of the FET in use to find out its breakdown voltage. Also note that the farther the gate-source voltage, VGS, is from the 0V, where the maximum drain current ID occurs, the lower the breakdown voltage is to enter the breakdown region.
