What is the Gate-Source Voltage, VGS , of a FET Transistor?
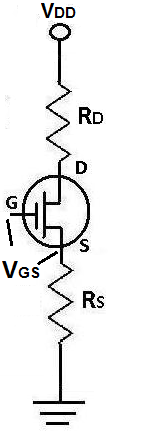
The gate-source voltage, VGS, of a FET transistor is the voltage that falls across the gate-source terminal of the transistor, as shown above.
The gate-source voltage, VGS, is a very important voltage because it is the voltage which is responsible for turning off a JFET or a depletion MOSFET transistor.
JFETs or depletion MOSFETs are normally on devices. This means that by connecting their terminals to a circuit, they will normally conduct current across drain to source, without any voltage provided to the base. To turn off these FET transistors, you apply a voltage (VGS) to the gate-source terminal, called the cutoff voltage, which stops the large drain-source current.
For N-Channel JFETs and depletion MOSFETS, the gate-source voltage needed to turn a transistor off is a negative value. This value ranges anywhere from -0.5V to -10V, depending on the specific FET used. For P-Channel JFETs and depletion MOSFETs, the gate-source voltage needed to turn the transistor off is a positive value. This value ranges anywhere from 0.5V to 10V, depending on the specific FET used.
Again, the gate-source voltage, VGS of a FET transistor is an
important voltage and is also used
in many calculations for FET calculations, such as the drain current ID, the drain-source
resistance RDS, and the transconductance of a FET, gm.