What is the Saturation Region of a FET Transistor?
>
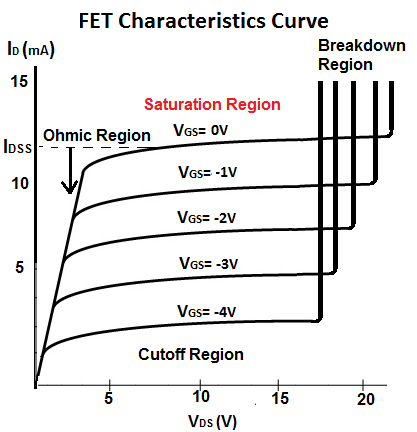
The Saturation Region of a FET transistor is the region where the drain current, ID, flowing from the drain to the source of the FET transistor, is the highest for the gate-source voltage, VGS, that is supplied.
This is why it is referred to as the saturation region, because the drain current output is at saturation, or maximum, output for the given voltage.
When you view the above characteristics curve for the above FET transistor, which in this case is a N-Channel JFET, the largest drain current I D occurs when the gate-source voltage, VGS, supplied is 0V. On the chart above, this would produce the current, called IDSS, and it's approximately equal to 12mA. The saturaton current when VGS= -1V is approximately 8mA. The saturation current when VGS= -2V is approximately 6mA. The saturation current when VGS= -3V is approximately 4mA. The saturation current when VGS= -4V is approximately 2mA.
In the saturation region, the FET transistor is strongly influenced by gate-source voltage, VGS, but hardly at all by the drain-source voltage, VDS.
The saturation region makes up the active region of the FET, where the transistor is in the On state.
