What is the Zener Voltage, VZ , of a Zener Diode?

The Zener Voltage, VZ, of a zener diode is the breakdown voltage of a zener diode when it is connected in reverse-biased in a circuit.
The reason the breakdown voltage of a zener diode is so important is because once the voltage that falls across a zener diode exceeds its breakdown voltage, the voltage across the zener remains constant, even if the current going through the zener diode continues to increase.
Because the zener diode holds its zener voltage so steady and constant, it has huge application in circuits, most importantly, voltage regulation.
Below is the voltage-current characteristics curve of a zener diode:
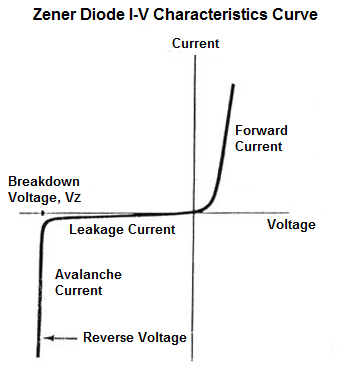
You can see in the above curve the how steady and constant the voltage across the zener diode is after it reaches the breakdown voltage, despite large changes in current.
This makes the zener diode very useful in circuits where steady voltages need to be supplied.
The zener voltage of zener diodes comes in a range of values. You can find them in 3.3V-12V easily in widespread use.
The circuit below has a zener voltage of 5.1V.
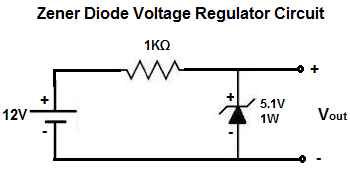
Therefore, the 12-volt power supply drops 5.1V and the voltage across the zener remains constant at this voltage. This 5.1 zener voltage is then placed in parallel to a load device, which it powers. This is a voltage regulator circuit.
The zener voltage of the diode can be any voltage, as is needed to be constant and power a circuit.
Related Resources
What is the Resistance, RZ, of a Zener Diode?
What is the Current, IZM of a Zener Diode?
What is the Power Rating, PZM, of a Zener Diode?
Zener Diode I-V Characteristics Curve
How to Build a Zener Diode Voltage Regulator