Capacitor Discharge Equation

The Capacitor Discharge Equation is an equation which calculates the voltage which a capacitor discharges to after a certain time period has elapsed.
Below is the Capacitor Discharge Equation:

Below is a typical circuit for discharging a capacitor.
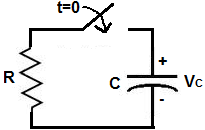
To discharge a capacitor, the power source, which was charging the capacitor, is removed from the circuit, so that only a capacitor and resistor can connected together in series. The capacitor drains its voltage and current through the resistor.
Variables in Capacitor Discharge Equation
Taken into account the above equation for capacitor discharge and its accompanying circuit, the variables which make up the equation are explained below:
- VC- VC is the voltage that is across the capacitor after a certain time period has elapsed.
- V0- V0 is the initial voltage across the capacitor before the discharging begins where it's connected in series with a resistor in a closed circuit. In simple terms, this is the voltage that the capacitor initially has before the discharge process begins.
- Time, t- Time, t, is the period of time which has elapsed since the discharge process has begun. t is measured in unit seconds. It is a very important parameter in this equation because it determines how much the capacitor discharges. The more time that has elapsed, the more the capacitor will discharge. Conversely, the less time that has elapsed, the less the capacitor will have discharged.
- Resistance, R- R is the resistance of the resistor to which the capacitor is connected to in the circuit, as shown in the diagram above. This affects the discharging process in that the greater the resistance value, the slower the discharge, while the smaller the resistance value, the quicker the discharge, and, thus, the lower the amount of voltage, VC, across the capacitor.
- Capacitance, C- C is the capacitance of the capacitor in use. C affects the discharging process in that the greater the capacitance, the more charge a capacitor can hold, thus, the longer it takes to discharge, which leads to a greater voltage, VC. Conversely, a smaller capacitance value leads to a quicker discharge, since the capacitor can't hold as much charge, and thus, the lower VC at the end.
These are all the variables explained, which appear in the capacitor discharge equation.
Again, if you want a quicker discharge time for a RC circuit, use a small resistance value for the resistor, a small capacitance value for a capacitor, and a lower initial voltage across the capacitor before discharge begins, for the variables you can control, for the reasons explained above.
If you want a longer discharge time for a RC circuit, use a large resistance value, a large capacitance value, and a large initial voltage across the capacitor.
The discharge time which you'll need depends on the specific application for which the RC circuit is used for.
Related Resources
Capacitor Impedance Calculator
Capacitive Reactance
How to Calculate the Current Through a Capacitor
How to Calculate the Voltage Across a Capacitor
Comment