How to Build a Common Cathode RGB LED Circuit

In this project, we are going to build and operate an RGB LED circuit using manual switches.
An RGB LED is an LED that can light up either red, green, or blue.
The type of RGB LED we will use in this circuit is a common cathode RGB LED. This is an LED in which all the grounds of the LEDs are tied together common.
Depending on which anode gets +3V determines which color the LED lights as.
The RGB LED is a dynamic LED because of the fact that it can light up to many different colors. Therefore, if you need multiple colors to be shown and if you have very limited space on a board (where you can't fit 3 separate LEDs), an RGB LED works perfectly.
In this circuit, we will use toggle switches to control the RGB LED. We can turn on one toggle switch at a time, 2 at a time, or all 3 at a
time. If we turn on one, only that color will light up. If we turn on multiple LEDs, all the selected LEDs will turn on.
Components Needed
- Common cathode RGB LED
- 3 220Ω resistors
- 3 toggle switches
The RGB LED is a 4-pin LED.
For the common cathode RBG LED, one pin is ground (pin 2) and the other 3 pins are the anodes of the red, green, and blue LED.
The pinout of the common cathode RGB LED is shown below.
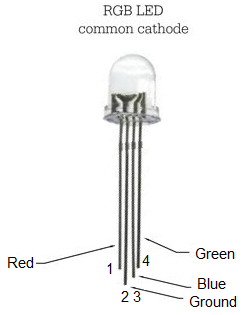
The RGB LED we are using is a common cathode LED. This means that all the grounds of the LED are tied together, i.e. they are common. We have to connect all of the anodes of the LEDs to sufficient positive voltage, which in this case is 3V.
The diagram at the following link shows the internal layout of the RGB LED:
Internal Diagram of a Common Cathode RGB.
So with common cathode RGB LEDs, we connect pin 2 to ground. This grounds all of the LED grounds. And then we connect all of the toggle
switches to positive voltage and ground, so that we can turn off or on whichever LED.
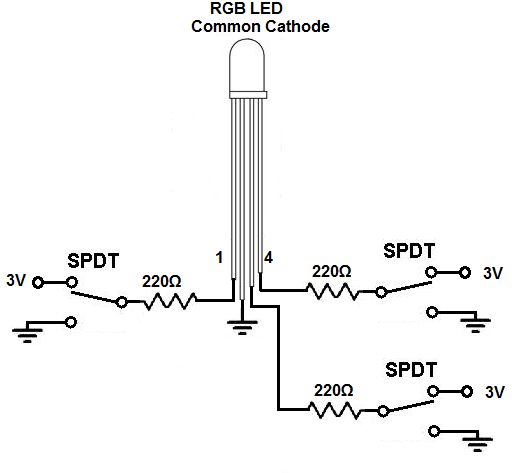
Common Cathode RGB LED Circuit
The common cathode RGB LED circuit we will build with manual switches is shown below.
This above circuit built on a breadboard is shown below.
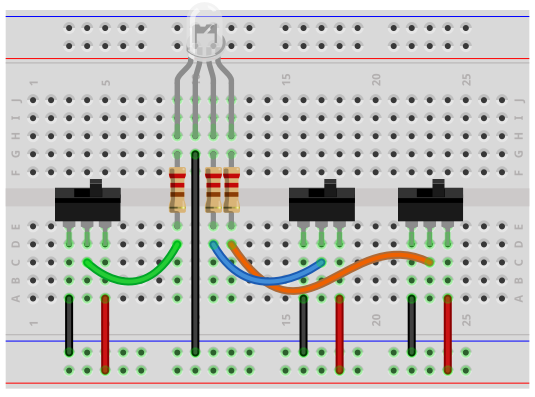
The connections are pretty simple.
We connect the ground pin (pin 2) of the RGB LED to ground. This grounds all of the LEDs pins.
We then connect toggle switches to each of the other pins, which are the anodes of each of the 3 LEDs.
To connect the toggle switches, we ground one of the terminal pins. We connect the other terminal pin to the positive voltage source through a 220Ω resistor. We then connect the middle pin to the anodes of each of the LEDs.
How the circuit operates is that when we turn the toggle switch to the positive voltage end of the toggle switch, the LED will turn on. This is because pin 2 is grounded. When the toggle switch is flipped to +3V, there is a potential difference and current can flow. When the toggle switch is flipped to the ground end of the toggle switch, both ends are at ground and there is no electrical difference. Therefore, the LED is off.
The 220Ω resistors function as current-limiting resistors, so that excess power don't go to the LEDs.
We can have all LEDs off, in which case the RGB LED does not light up at all.
Or we can turn on one LED at a time, in which case that color alone will show, whether it's red, green, or blue.
Or we can turn on any combination, 2 at a time, all 3 on at once.
When we turn on multiple LEDs, the colors that are on will show.
And this is how an RGB LED works.
Related Resources
How to Build a Common Anode RGB LED Circuit
