Fetal Heart Rate Variability

Heart rate variability is the amount in beats per minute (bpm) that the heart rate varies in a given period of time.
In this article, we're specifically talking about heart rate variability in terms of a fetus.
So if the heart rate goes as high as 160 bpm to 140 bpm in a given time period, there is a difference of 20 bpm or a variability of 20 bpm.
Variability is important because it helps to show the status of a fetus.
One of the most important ways to measure the status and well-being of an infant is the heart rate. And specifically, when looking at the heart rate, we want to see a degree of variability, because this shows the infant is moving, which is resassuring.
There are 3 types of variability that exist in reference to the heart rate and it's classified by the amount of variability there is.
The first type is absent variability. Absent variability means that there is a difference between 0 and 5 bpm in a fetus's heart rate for a given period of time.
The second type is moderate variability. Moderate variability means there is a difference between 6 and 25 bpm in a fetus's heart rate for a given period of time.
The third type is marked variability. Marked variability means there is a difference greater than 25 bpm in a fetus's heart rate over a given period of time.
When assessing the heart rate of a fetus, we want to see some variability, because variability is a sign that the baby is moving around and is well. Moving around, such as kicking, increases heart rate, because movement increases oxygen demand. In order for the body to meet this oxygen demand caused by movement, it must pump blood through the body quicker. The body does this by increasing the heart rate, so oxygen can be pumped more efficiently through the body.
So we do not want to see absent variability, because this could signal that the fetus isn't moving much, which may be a sign of concern.
Factors that could decrease variability include fetal sleep, narcotics, or other sedative drugs, alcohol and other illicit drugs, fetal sepsis, fetal tachycardia, gestation less than 28 weeks, any anomalies to the fetal central nervous system regulation of the heart rate, and hypoxia that is severe enough to affect the central nervous system.
Narcotics can cause depression to the central nervous system (CNS). This, in turns, causes less fluctuations in rises in heart rate. Sedatives can cause the same effect.
Alcohol, and many other illicit drugs, are depressants. Therefore, they can cause less increases in heart rates.
So these are a few factors that can affect heart rate variability. Therefore, you can see pretty easily how a lack of variability can signify very serious potential conditions.
So a lack of variability should prompt a healthcare worker to further investigate if see any of the above issues can be affecting the fetus.
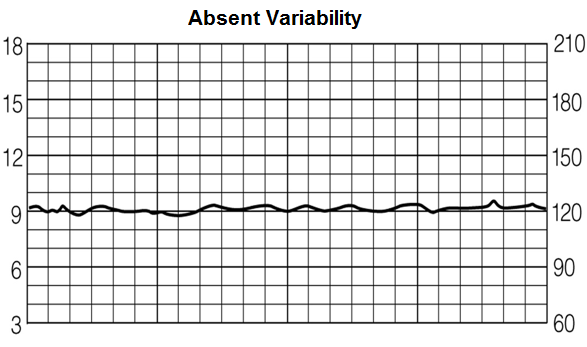
Absent variability entails a heart rate that varies between 0 and 5 beats per minute (bpm).
You can see on this chart how the heart rate goes as high as 124 beats and then goes as low as 119 beats.
This is a difference of 5 beats per minute. So since the difference is between 0 and 5 bpm, this represents absent
variability.
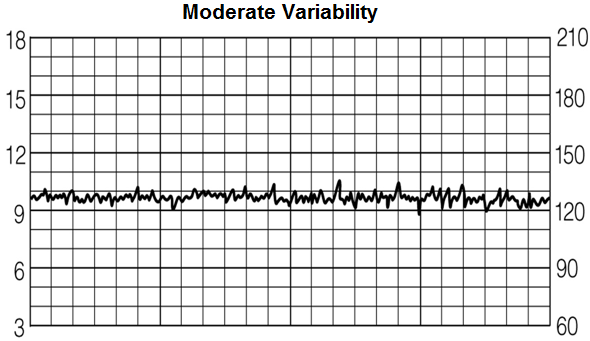
Moderate variability entails a heart rate that varies between 6-25 beats.
You can see on this chart how the heart rate goes as high as 136 beats and then goes as low as 118 beats.
This is a difference of 18 beats per minute. So since the difference is between 6 and 25 bpm, this represents moderate
variability.
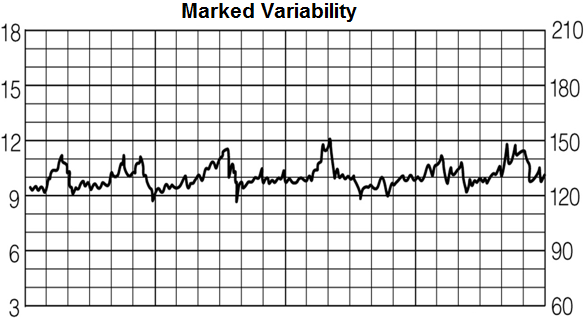
Marked variability entails a heart rate that varies greater than 25 beats per minute.
You can see on this chart how the heart rate goes as high as 151 beats and then goes as low as 118 beats.
This is a difference of 33 beats per minute. So since the difference is greater than 25 bpm, this represents marked
variability.
Related Resources
Early Decelerations- Explained
Late Decelerations- Explained
Variable Decelerations- Explained
