How to Retrieve Data Asynchronously from a MySQL Database Using AJAX and PHP

| Enter a Username: | |
| Choose a Password: |
In this article, we show how to retrieve data from a MySQL database using AJAX and PHP.
Through AJAX, we can make asynchronous requests to the server to get information from the server such as in a database like a MYSQL database.
This way, a user can keep on working while information in a page updates without the page having to be refreshed.
So AJAX is a powerful language that allows us to send asynchronous requests to a server so that a browser can get information from the server without the page having to be refreshed.
In order for AJAX to work, 2 languages must be used, a client-side language (this is Javascript) and a server-side language such as PHP or ASP.net. The thing about AJAX is it allows a programmer to combine a client-side language with a server-side language to get the benefits of both and combine in them.
With AJAX, client side triggers can get server-side information.
So AJAX allows like the best of both worlds.
It's like Javascript being a client and server side language at the same time. But it's not Javascript working alone. It's javascript doing the client side work while making a request to the server (through the browser) to get information from the server (such as a database like a MySQL database). We then let a server-side language take over to get the server side information and return it to our page.
So this is the benefits of AJAX.
It allows us to update a page without refreshing because we communicate asynchronously with the server while a user continues to work.
So looking at the form above, you see a standard like registration page, where you choose a username and a password.
With AJAX, we can check a database to see if the username that the user has entered is already taken asynchronously. If it already exists in our database, then it's already taken and a user can't select it. Therefore, we want to update this information right away to the user, so that s/he can change it and select another username without having to click Submit and have the page refresh and find out that it's already taken.
This form uses the javascript onblur() function for the username text box, which means that the ajax function is called when the user clicks on the box, writes something, and then clicks off the box, usually to then write in the password necessary. When the user does this, AJAX updates the username box so that the user knows whether that name has been taken already or not. Again, this is all done without the page having to be refreshed.
For this username box above, the usernames that are already taken are john, peter, adam, rodney, david, jeff, joseph, and bob. If you type in these usernames and click away from the box, you will get the message that they are already taken. If you enter in anything else, you will get the message that the username is available. All again done without the page having to be refreshed.
This is actually a very common use of AJAX in many websites. Many websites want users to know information right away without a user having to make a synchronous request by filling out a whole form, clicking the Submit button, and finding out that some information can't be used. It's not as efficient as just letting the user know right away. Therefore, many, many websites use AJAX for this reason, as well as for many other things.
So AJAX is widespread on the web and very useful.
So now we will show how to go about getting information from a MySQL database using AJAX and PHP.
So how do we do this?
MySQL
So first let's go over what I did in my MySQL and it's very simple.
So in MySQL, I created (actually used an existing) database and created a table called Usernames.
This table is composed of 3 columns, ID, username, and password.
The ID column is of type INT(11), username VARCHAR(50), and password VARCHAR(50).
The structure of the table can be seen below.
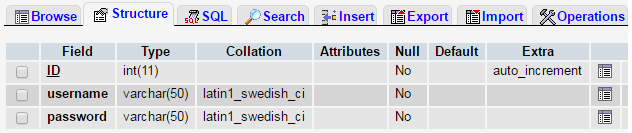
The entries listed in the Usernames table is shown below.
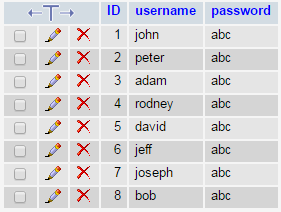
These are all the usernames that are currently in the MySQL table.
So this is all that has to be done in the MySQL side of the code. I did this using phpMyAdmin.
You can do the same or something similar.
HTML and Javascript Code
The HTML and Javascript code to create the username and password text boxes as well as to call an asynchronous request when the user clicks away from the text box is shown below.
So this is all the Javascript and HTML code needed to create asynchronous requests for our username registration form.
We'll now go through each line of code so that you understand what each does.
So we add <script> tag to our code to indicate that we're going to add Javascript to the page. Any type of Javascript entry requires an opening and closing script tag.
We then create a function called checkUsername(). This function, as it's named, is designed to check the username that a person enters to see whether the username has been registered already or not. If it has, the user cannot take it. If it hasn't, the username is available. If this text box is left empty, a message will be shown telling the user that a username must be entered into this field. This is how many real-world registration forms work for many of the biggest companies and websites in the world.
The first thing we do in this function is create a variable called request. This variable will represent a request object, which is absolutely imperative in order for the browser to request communication with the server. Otherwise, AJAX is impossible. The request object is pretty much the heart of AJAX.
The most common way to create a request object is through the line, request= new XMLHttpRequest(); Through this line, most browsers can create a request object, which then can be called so that a browser can communicate with the server. However, this line may not work for all browsers. Therefore, we use try catch statements to create a request object by other means in the event that the browser cannot do so through the first way. So we try also the tryMicrosoft function and the otherMicrosoft function. These are more specific to Microsoft browsers such as Internet Explorer for creating a request object. If all the methods fail, the last method failed is run, which makes the request object equal to null; if this happens, asynchronous communication cannot occur because the browser has no way of contacting the server. However, if you are using any type of major browser, this shouldn't happen. You should be able to create a request object.
You'll see how this request object is used later in the code. But if you want a full in-depth article on request objects, see How to Create a Request Object in AJAX.
So after we've created a request object, we then create a variable called url, which contains the name of the PHP file that processes our data. I named my file, process.php.
Next, a variable named user has been created which stores the value that the person enters into the username text box.
We then create a variable called pw, which stores the value of the password that the user enters into the password text box.
We then create a variable called vars. This variable will stores the values of the username and the password. This variable is written as a name=value pair. The name=value pair is the username. Since the username equals the variable user, the total statement "username="+url. In between each name=value pair has to be an ampersand (&). This separates the different name=value pairs. The second name=value pair that we send is the "password="+pw.
This variable vars is very important and in fact can be seen as the heart of the PHP file, process.php, that processes our request. Using this vars variable, we can have PHP parse this variable and extract the data from it. Thus, from this vars variable, we can know what a user enter into these username and password text boxes. We'll show how to do this in PHP when we get to the PHP code.
Next we take the request object and use the open method on it. This open method decides whether we use the POST or GET method. It takes the URL that we want parsing the data that we submit to. And it determines whether the request should be asynchronous or not. By making the third parameter true, the request becomes an asynchronous request which is what we desire.
The line, request.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");, is just for character encoding of the variable vars we are sending. For the vars variable, it is organized in name1=value1&name2=value2&name3=value3 order. Now say for instance, that the value had the ampersand symbol (&), this could throw off the vars variable and cause an error. To protect against this, we put this line in the code.
Next, we take the request object and find its onreadystatechange property and set it equal to function(). The onreadystatechange property is a property that changes as the server processes a request by a browser. It has 4 states, 1 is the first inital state and 4 means it's absolutely ready. If request.readyState is equal to 4, this means that the server has obtained the request object from the browser and is ready to process the data sent. There is also another property named status that we can check to determine if everything is in place. If ready.status is equal to 200, this means that all is OK. Once these 2 parameters are in place, we create a variable called return_data and set it equal to request.responseText. The responseText variable is the data which the PHP file returns. Let's say you have a PHP file processing this request and in turn you set so that the PHP file echos a certain statement such as, "Everything has been processed well." This statement then goes into the responseText, which receive back after everything has been processed on the server side. So the return_data is very important. It's the output of the PHP file that processes the request on the server side.
We then take the Javascript document.getElementById() function to get the element on our HTML page that has the Id of status. We place this right next to the username text box that has the HTML label tag. This label tag has the Id of status. We access the contents of this label tag through .innerHTML. This property lets us write data to the HTML label tag that has the Id of status. We then set it equal to return_data, which is the data that the PHP file echoes out.
The last statement, request.send(vars);, is the statement that actually executes the sending of the vars variable, so that the PHP file can process it. So it isn't actually sent until this statement.
So this is all that is required on the HTML and Javascript.
The last thing we have is the PHP code.
PHP Code
So the last thing we have is the PHP code, which is the server side language that can actually speak to the server.
Javascript cannot manipulate server information. A server side language is needed, and that's PHP.
So we need a server side language to ge the data from the server, so that we can process this data and output a result based on this data.
The PHP code that we use is shown below.
So this is our PHP code above.
The first line uses a PHP variable called $username_entered. It gets the value of the username that the person has entered in the form. Remember that the vars variable contained, var vars= "username="+user+"&password="+pw; PHP is able to extract the data that the person has entered into the username text box through the name=value pair. So all we have to do is create a PHP variable and set it equal to the value of the name of the pair. So we set the $username_entered variable to $_POST['username']; PHP will then get the value that the person has entered into the username form. The same is true for password. We create a variable named $password_entered and set it equal to $_POST['password']. Password is the name attribute of the password entered into the password text box.
Since we are retrieving data using PHP from a MySQL database, we have to set up connection to the database. This requires a username, password, hosting name, database, and table name (of the table we want to retrieve data from).
We then connect to this database via the mysql_connect() function and @mysql_select_db() function.
We then create a variable $result which is a query to the table we selected. We use the mysql_query() function to query this table. We select the column username on our table and use the WHERE clause to find out if the username column has a username that the person has entered into the form. So this is the query. We then count the number of rows that the table has returned based on this query using the mysql_num_rows() function. If the number of rows is 0, we know that this username doesn't exist in the table and, thus, the user can selct it, since it's available. Else if the count isn't 0, this means that this username exists already and cannot be taken.
So now we use a series of if statements to determine what our PHP file will output.
The first we want to do is cover whether the username is empty or not. This covers the case that the user clicks on the username text box, inputs nothing, and clicks away from it. In the event that the user does this, we echo out the statement, "A username must be entered into this field". Else if the username text box isn't empty and the count is equal to 0, we echo out that the username is available. The $count variable is equal to 0, because the username doesn't exist. The query function went through the table and didn't return an instance of that username which was entered. The next statement, an else statement, echos out that the username is already taken if the count isn't equal to 0. In this case, we echo out that the username is already taken and to please select another username.
So this is all that is required to retrieve data asychronously from a MySQL database using PHP and AJAX.
This form has been greatly simplified. It doesn't have any functionality, because it's just made to demonstrate AJAX. It doesn't process the data and logs you in. I also added no functionality to the password text box, so it won't work. It was just done to demonstrate the power of AJAX with the username text box. So keep that in mind.
But this code shows the huge power of AJAX in applications for the web to retrieve data asynchronously, for all asynchronous requests.
Related Resources
How to Insert Data into a MySQL Database Using AJAX and PHP
