What is VBE of a Transistor?
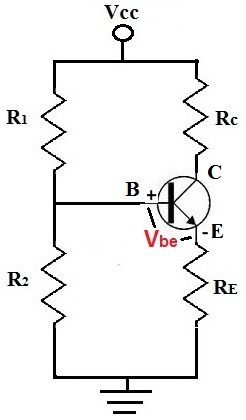
VBE is the voltage that falls between the base and emitter of a bipolar junction transistor.
VBE is approximately 0.7V for a silicon transistor. For a germanium transistor (which is more rare), VBE is approximately 0.3V.
VBE is important when doing DC analysis of a transistor circuit because it is used for calculations to find the transistor's DC values. One of the most important calculations it is used for is to find the quiescent current of the transistor, IEQ. IEQ can then be used to find other values in the circuit such as VCEQ or IB. The calculation is shown below:
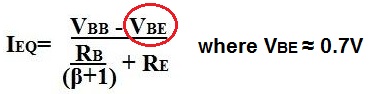
Again, this formula, can be used for either silicon or germanium transistors. The example above showing 0.7V for VBE is of a silicon transistor.
Related Resources
What is VBB of a BJT Transistor?
What is VCC of a BJT Transistor?
What is VCE of a BJT Transistor?
What is Vπ of a BJT Transistor?
What is hFE of a BJT Transistor?
What is β (beta) of a BJT Transistor?
What is α (alpha) of a BJT Transistor?
What is gmVπ of a BJT Transistor?
