What is VCC of a Transistor?
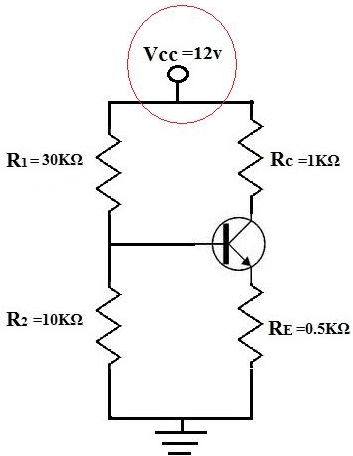
VCC of a bipolar junction transistor is the DC voltage that is supplied to the collector of the transistor.
VCC is a very important voltage when biasing the transistor because it determines how much the AC signal can be amplified to in the transistor. If VCC is too low, the transistor will not have enough power and the amplified AC signal will come out clipped.
VCC normally does not have to be calculated in a transistor circuit, as it's normally just given. However, it is very important when calculating other values in a transistor such as IC, the current through the collector and Ie, the current through the emitter. VCC is also important for calculating the load line of the transistor and thus its Q-point.
Related Resources
What is VBB of a BJT Transistor?
What is VBE of a BJT Transistor?
What is VCE of a BJT Transistor?
What is Vπ of a BJT Transistor?
What is hFE of a BJT Transistor?
What is β (beta) of a BJT Transistor?
What is α (alpha) of a BJT Transistor?
What is gmVπ of a BJT Transistor?
What is Open Collector Output (of a BJT Transistor)?
