Bernoulli Trial Calculator
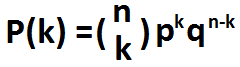
This Bernoulli Trial Calculator calculates the probability of an event occurring.
The formula for calculating the result of bernoulli trial is shown below:
![]()
The bernoulli trial is calculated by multiplying the binomial coefficient with the probability of success to the k power multiplied by the probability of failure to the n-k power.
![]() represents the binomial coefficient. The binomial coefficient represents the total different number of combinations we can take k items from a total of n selections. For example, if we have
a total of 7 items and we want to choose 5 items from those 7, then n=7 and k-5, and the binomial coefficient would be equal to 21. This means there are 21 different possible combinations we
can arrange 5 items when taken from a total of 7 items.
represents the binomial coefficient. The binomial coefficient represents the total different number of combinations we can take k items from a total of n selections. For example, if we have
a total of 7 items and we want to choose 5 items from those 7, then n=7 and k-5, and the binomial coefficient would be equal to 21. This means there are 21 different possible combinations we
can arrange 5 items when taken from a total of 7 items.
pk represents the probability of the event occurring. It represents the success rate that the event occurs.
qn-k represents the probability of the event not occurring. It represents the failure rate of the event.
When we take all of these variables and multiply them together, we get the result of bernoulli trial. The bernoulli trial represents the probability of success (that an evil will occur).
Bernouill trial computation can only done under the following circumstances.
- 2 outcomes only- When there only only 2 possibile outcomes, most of the time expressed as success or failure. This can represent many different results such as heads or tails, win or lose, go or don't go. It can only be done when there are exactly 2 outcomes. Most of the times it will be expressed as success or failure.
- Each trial must be independent- Each trial (each time the event occurs) must be independent of each other. This means that the events are completely independent; they do not depend on the previous trial or the trial after. A classic example is heads or tails. Each flip is independent of all others.
- Probability of success is the same for each trial- The probability of the event occurring or there being success in the desired outcome must be the same. For example, for each flip of a coin, there is always a 50% success rate of getting a heads. In other words, the probability of an event occurring must be the same, not different, for each trial.
If all of these conditions are met, we can apply bernoulli trial to finding the percent outcome that an event will occur.
To illustrate bernoulli trial, let's go through an actual example where bernoulli trial would be used.
Let's say there is an exam where 60% of students pass. This is the freshmen entrance exam. If 7 freshmen take the examm, then what will the probability be that 5 pass. In this example, n=7, k=5, and the success rate is 60% or .6. The failure rate then will be 1-.6=.4 or 40%. Using these numbers, we plug them into the formula. The binomial coefficient of n=7 and k=5 will be 21. We then have P(k)= 21(.6)5(.4)2= .2613 or 26.13%. This 26.13% is success rate that 5 out of 7 freshmen will pass the exam.
To use this calculator, a user simply enters in the n and k values, only with the probability that the event will occur. S/he then clicks the 'Calculate' button, and the resultant bernoulli trial calculation will be automatically computed and displayed.
Bernoulli trial can be used for any scientific calculations.
Related Resources
Confidence Interval Calculator
Variance Calculator
Standard Deviation Calculator
Expected Value Calculator
Z Score Calculator
Z Score to Raw Score Calculator
Chebyshev's Theorem Calculator
System of Equations Calculator
Factorial Calculator
Significant Figures (Sig Fig) Calculator
Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Test Statistic Calculator
Paired t-test Calculator
Unpaired t-test Calculator
